
Therefore, approximately $30 or $0.03 in extra costs increases the break-even price to $30.06, meaning $30.07 results in a profit. The break-even price of $30.03 presents the partial break-even price, as the investor will pay an additional 0.10% when selling the investment. Multiplying the required units by the unit price will also yield the necessary revenues to break even.Ī break-even point example for an unleveraged investment:Īssume an investor buys 1,000 shares in a company at $30 per share and pays a 0.10% commission when buying and selling. Subtracting the variable cost from the unit price and dividing it by the unit price provides the contribution margin ratio. The company will break even with $30,000 in revenues, meaning it neither recorded profits nor losses. Here is a break-even point revenue example (financial): Anything below 400 units results in operating losses for the company.
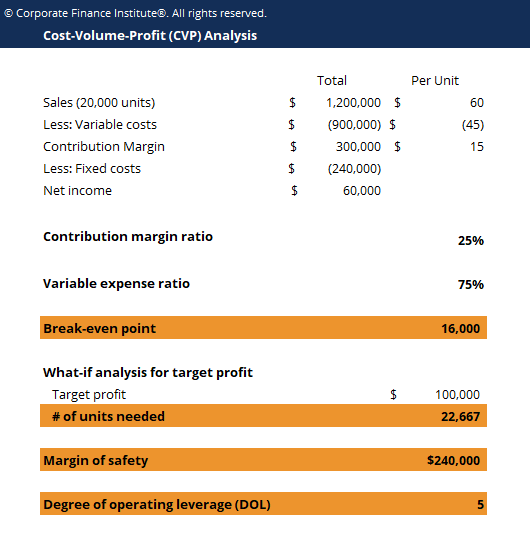
The company will break even with the 400 th unit sale and turn a profit from the 401st unit sale. Here is a break-even point unit example (accounting): Assume a company has fixed costs of $10,000, variable costs per unit of $50, and a sales price of $75 per unit.
#BREAK EVEN POINT FORMULA EXAMPLE HOW TO#
What is a break-even point in business? How about for an unleveraged investment or leveraged trade? Our below examples will illustrate how to find a break-even point.īusiness can either determine their break-even point by how many units they must sell or by required revenues. Trading costs impact the break-even price, especially for leveraged traders, where the break-even price increases each trading session. In finance, the entry price presents the starting point. In business, fixed and variable costs and the selling price impact the break-even point.
#BREAK EVEN POINT FORMULA EXAMPLE PLUS#
It applies to companies producing a good or service, but how do financial markets define a break-even point? In financial markets, the break-even point equals the current price minus the entry price plus trading costs.Ī break-even point applies when a good or service enters production, or traders and investors take a position. When the equation equals zero, the company has reached its break-even point, and each additional sale will result in a profit. The break-even point equals the total revenues subtracted from the total production costs. The break-even point, or the break-even price in financial markets, is the level representing neither a profit nor a loss exists. START TRADING NOW What is the Break-Even Point Definition?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
